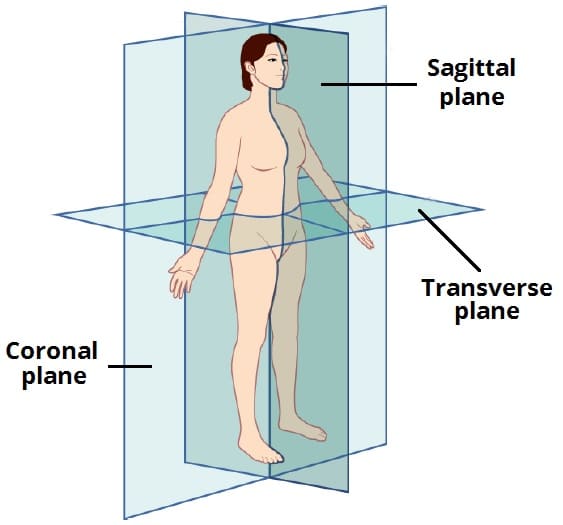
The anatomical planes are hypothetical planes used to describe the location of structures in human anatomy.
They are applied to the human body in the anatomical position.
In this article, we shall look at the anatomical planes in more detail – in particular, the three most commonly used planes: sagittal, coronal and transverse.
Sagittal Plane
The sagittal plane is a vertical plane which passes through the body longitudinally. It divides the body into a left section and a right section.
A specific sagittal plane is the median sagittal plane – which passes down the midline of the body, separating it into equal halves.
Coronal Plane
The coronal plane is a vertical plane which also passes through the body longitudinally – but perpendicular (at a right angle) to the sagittal plane.
It divides the body into a front (anterior) section and back (posterior) section.
Transverse Plane
The transverse plane is a horizontal plane. It is perpendicular to both the sagittal and coronal planes, and parallel to the ground.
It divides the body into an upper (superior) section and a lower (inferior) section.
Transverse planes are also known as transaxial planes or axial planes.