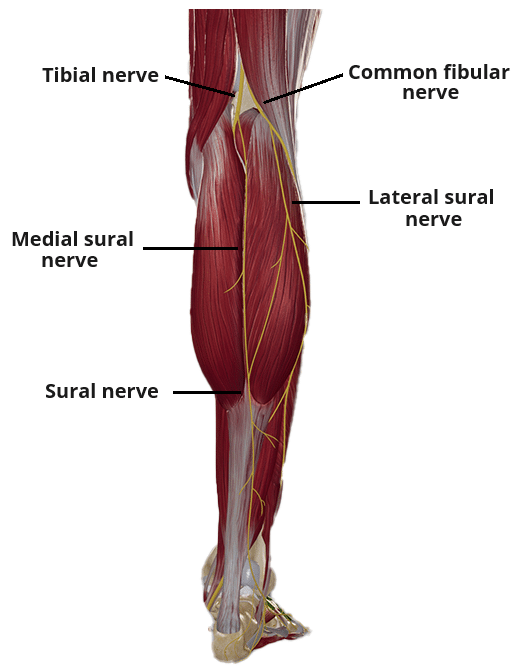
The sural nerve is a cutaneous nerve of the lower limb, formed by contributions from the tibial and common fibular nerves.
It supplies the skin over the posterolateral leg and foot.
Course
The sural nerve is formed by the convergence of two nerves:
- Medial sural nerve – arises from the tibial nerve and travels downwards between the two heads of the gastrocnemius muscle. It then penetrates through the deep fascia to lie superficially within the leg.
- Lateral sural nerve – arises from the common fibular nerve and travels over the lateral head of the gastronemius.
At the level of the distal third of the gastronemius (although this is variable between individuals) the medial and lateral branches combine to form the sural nerve.
The sural nerve travels within the subcutaneous tissue of the lower leg, accompanied by the short saphenous vein.
It passes posterior to the lateral malleolus and enters the foot – terminating as the dorsal cutaneous nerve.
Sensory Functions
The sural nerve supplies the skin of the posterolateral leg and the lateral aspect of the foot.