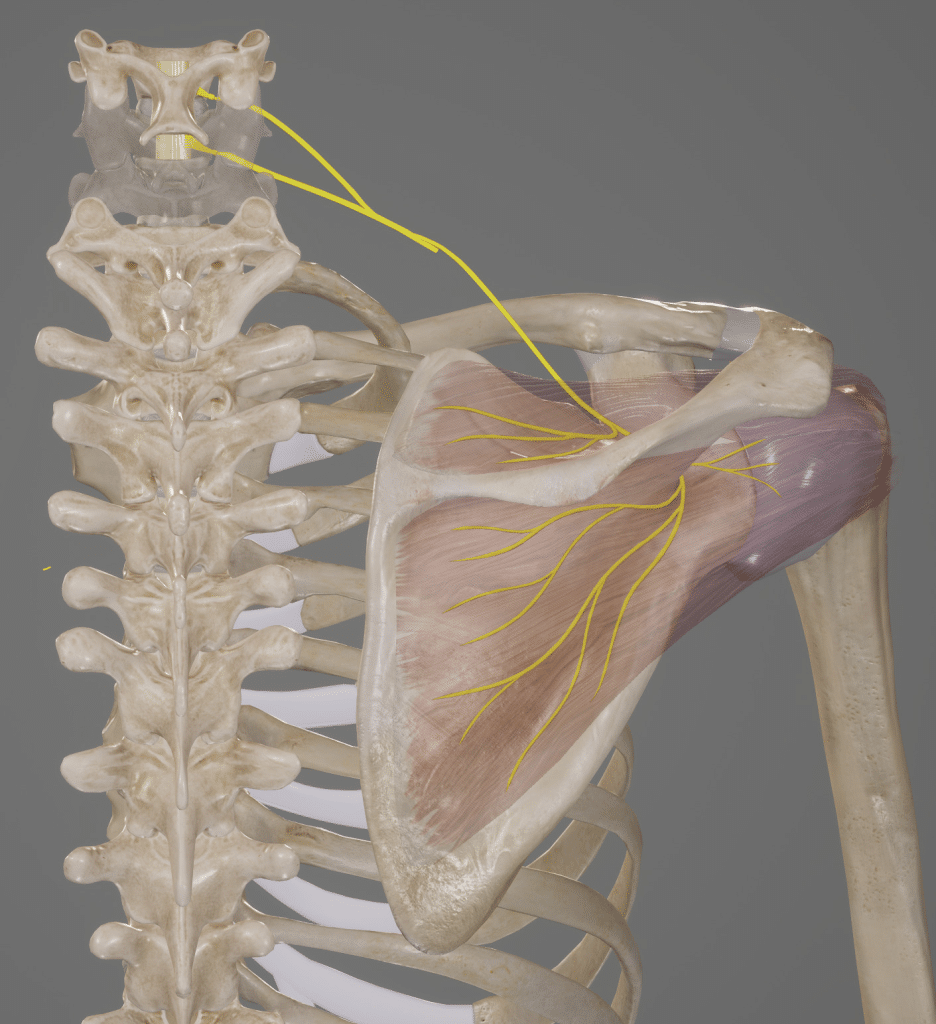
The suprascapular nerve is a mixed motor and sensory nerve arising from the superior trunk of the brachial plexus.
It supplies sensory innervation to the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints and motor innervation to the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles.
Course
The suprascapular nerve originates from the superior trunk of the brachial plexus in the neck, containing fibres from roots C5 and C6.
It first passes laterally across the posterior triangle of the neck. The nerve then travels underneath the trapezius muscle, before traversing the suprascapular notch to enter the suprascapular fossa.
It then continues along the superior border of the scapula, deep to the supraspinatus, through what is known as the suprascapular canal. Along this route, two nerves arise:
- Motor branch to supraspinatus
- Sensory branch to the acromioclavicular joint
Eventually the nerve reaches the spinoglenoid notch, where it supplies sensory fibres to the glenohumeral joint. It continues around the lateral border of the scapula to enter the infraspinous fossa.
The remaining nerve fibres travel medially to innervate the infraspinatus muscle.
Sensory Functions
The suprascapular nerve supplies sensory fibres to the glenohumeral joint and the acromioclavicular joint.
Motor Functions
The suprascapular nerve supplies motor innervation to the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles.
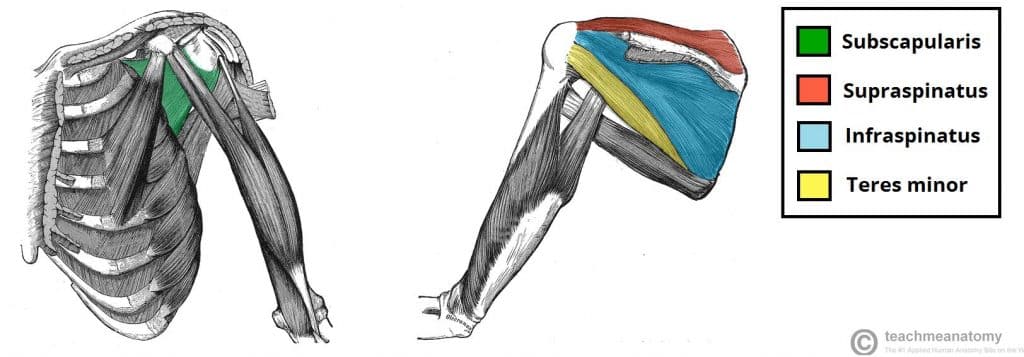
Fig 2 – The rotator cuff muscles, which act to stabilise the shoulder joint.