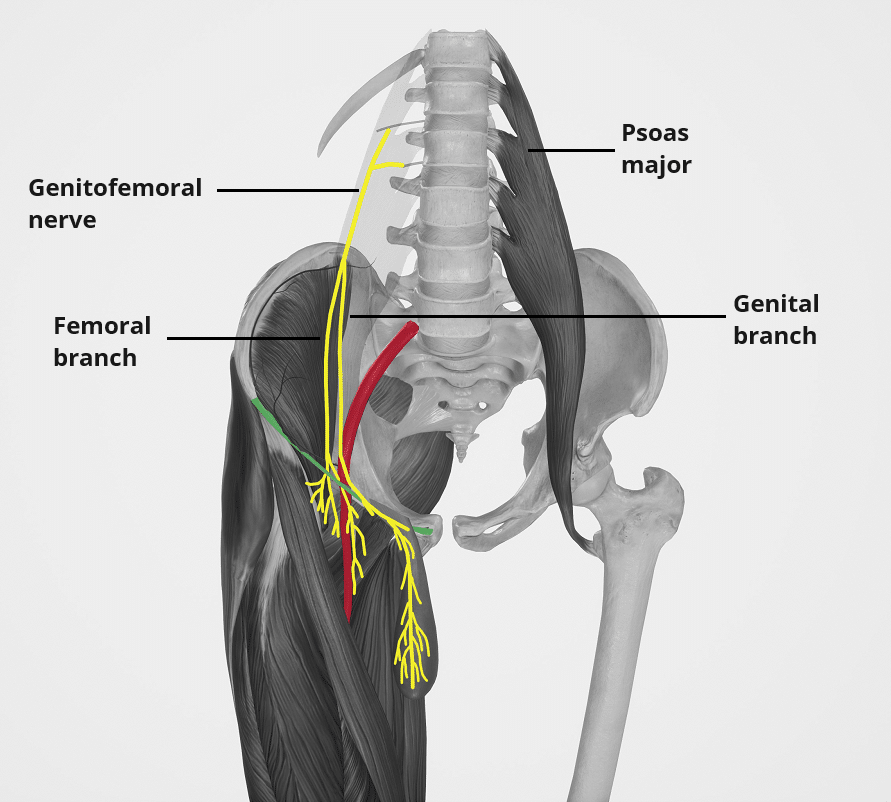
The genitofemoral nerve is a mixed peripheral nerve of the lower limb.
It contributes to the sensation of the thigh and genitalia, and innervates the cremaster muscle in males.
Course
The genitofemoral nerve arises from the lumbar plexus, containing fibres from spinal roots L1 and L2.
It travels inferiorly along the posterior abdominal wall, over the anterior surface of the psoas major muscle.
As the nerve reaches the inguinal ligament, it divides into two terminal branches:
- Genital branch
- Males – passes through the inguinal canal to reach the scrotum in males, where it supplies the cremaster muscle and sensation to the lateral aspect of the scrotum.
- Females – passes through the inguinal canal and supplies sensation to the mons pubis, labia majora and adjacent thigh.
- Femoral branch
- Passes underneath the inguinal ligament to reach the thigh, where it supplies cutaneous branches to the skin overlying the femoral triangle.
Sensory Functions
The femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve supplies cutaneous innervation to the skin overlying the femoral triangle.
In males the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve innervates the lateral scrotal skin. In females, it innervates the mons pubis, labia majora and adjacent thigh.
Motor Functions
The genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve innervates the cremaster muscle of the spermatic cord.
It is responsible for efferent limb of the cremasteric reflex – contraction of cremaster muscle and resulting elevation of testis upon sensory stimulation of the ilioinguinal nerve.