Search Results
Showing results 17 - 24 of 139
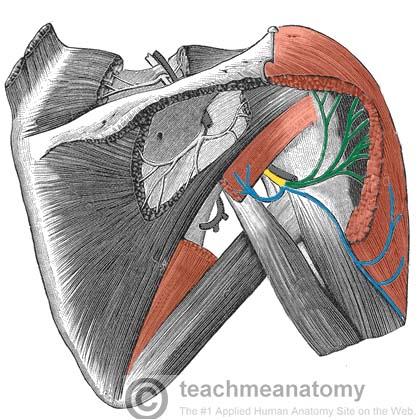
The Axillary Nerve
…medially to the surgical neck of the humerus, where it divides into three terminal branches: Posterior terminal branch – provides motor innervation to the posterior aspect of the deltoid muscle…
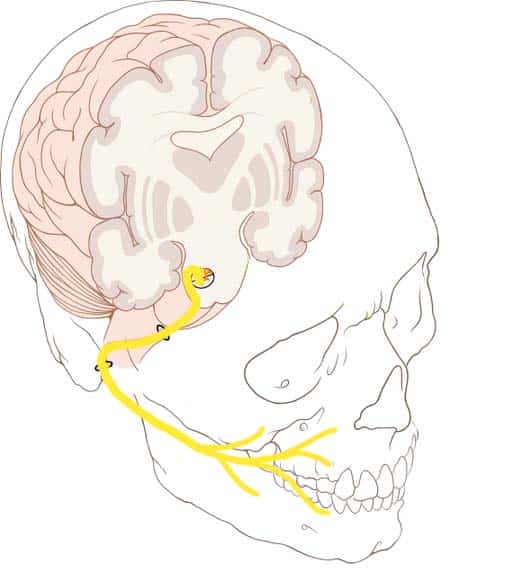
The Facial Nerve (CN VII)
…tympani Parasympathetic – supplies many of the glands of the head and neck, including: Submandibular and sublingual salivary glands. Nasal, palatine and pharyngeal mucous glands. Lacrimal glands. By Patrick J….
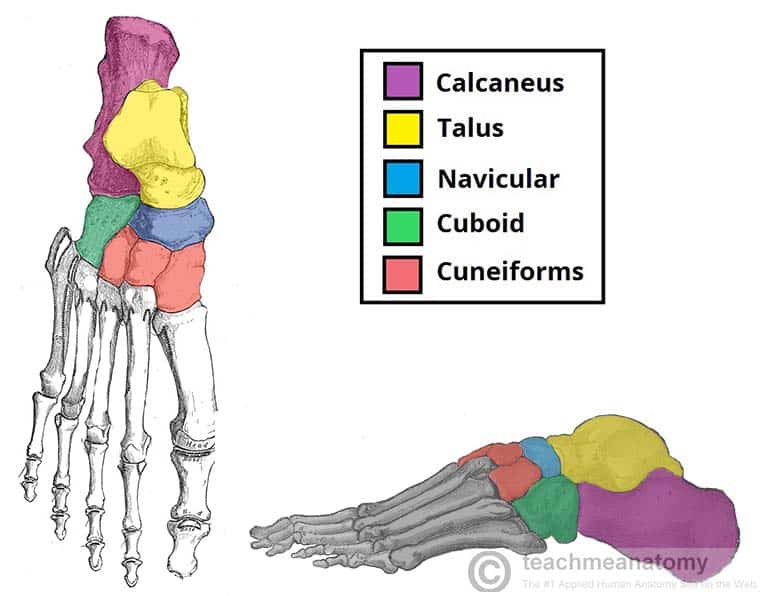
Bones of the Foot: Tarsals, Metatarsals and Phalanges
…the talar head are the least common. Talar neck fractures are typically high-energy injuries where the foot is forcibly dorsiflexed and the neck of the talus is pushed against the…
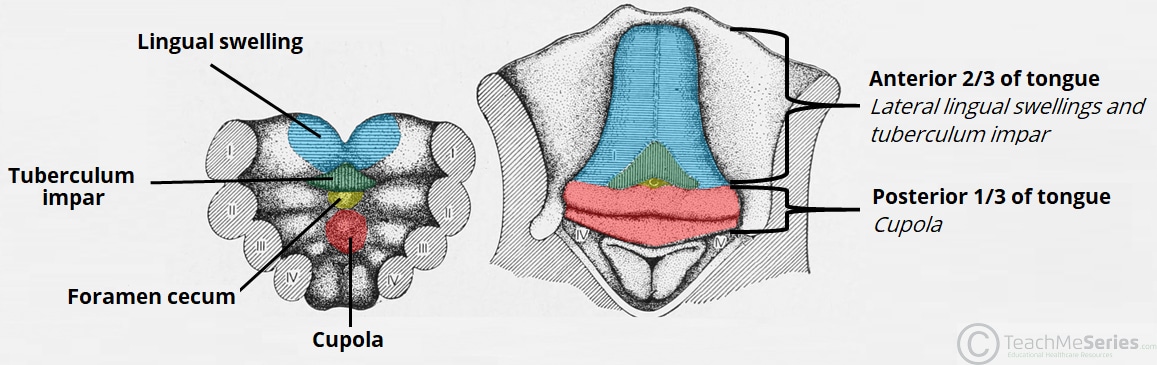
Development of the Pituitary, Tongue and Thyroid
…mesoderm in the region of the upper neck. The somites migrate from the neck anteriorly to give rise to the muscles of the tongue. Thyroid Gland The thyroid gland begins…
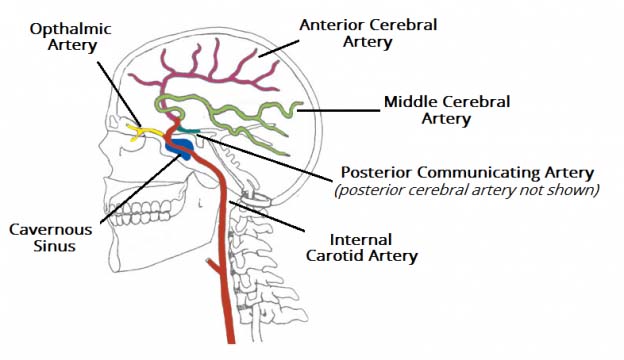
The Arterial Supply to the Central Nervous System
…the vertebral arteries, and the internal carotid arteries. These arteries arise in the neck, and ascend to the cranium. Within the cranial vault, the terminal branches of these arteries form…
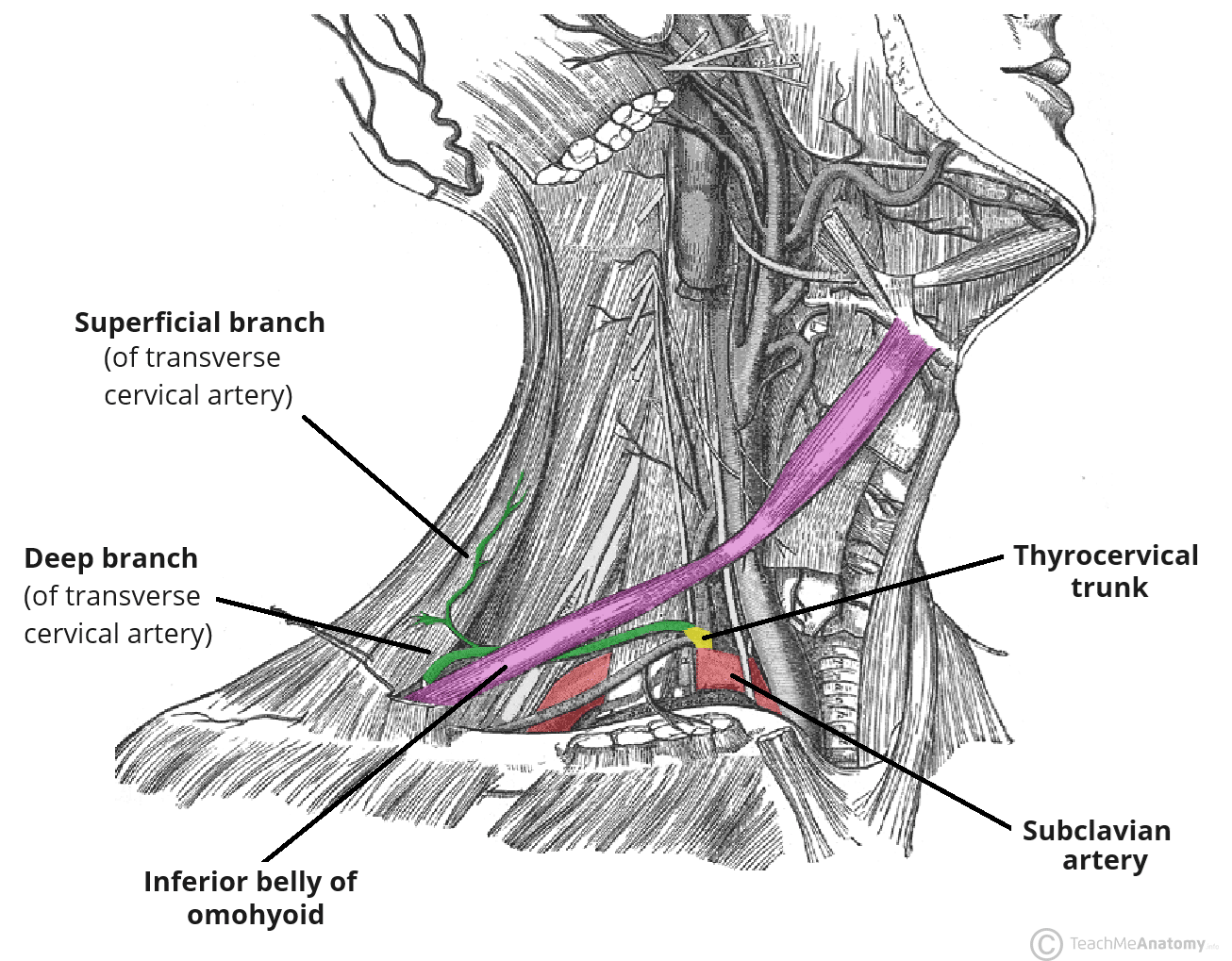
Transverse Cervical Artery
The transverse cervical artery (cervicodorsal trunk) is an artery of the anterior neck. It is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk. It contributes to the blood supply of the brachial…
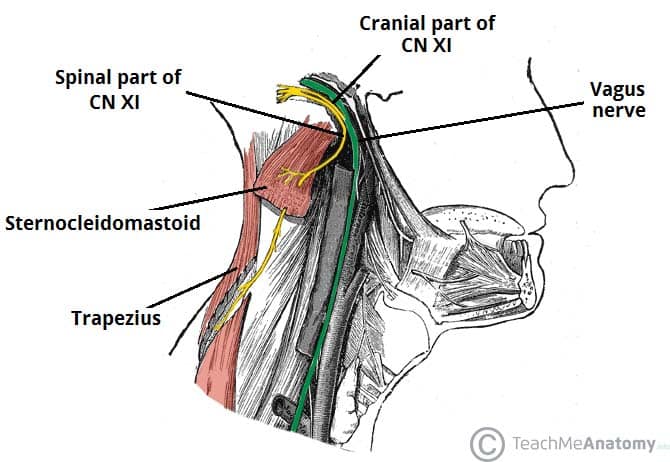
The Accessory Nerve (CN XI)
…which it innervates. It then moves across the posterior triangle of the neck to supply motor fibres to the trapezius. Note: The extracranial course of the accessory nerve is relatively…
Development of the Head and Neck
[child-pages depth=”1″]…
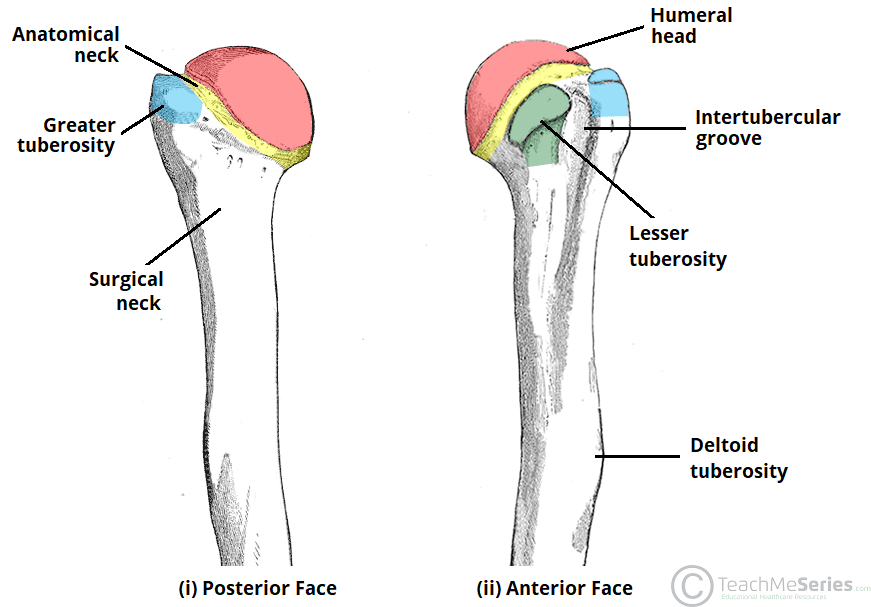
The Humerus
…of the humerus Proximal Landmarks The proximal humerus is marked by a head, anatomical neck, surgical neck, greater and lesser tuberosity and intertubercular sulcus. The upper end of the humerus…