Search Results
Showing results 1 - 8 of 71
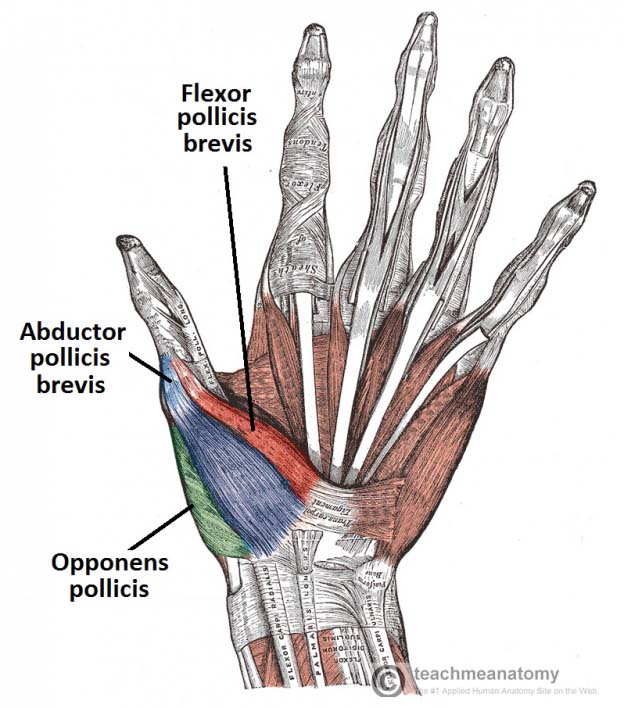
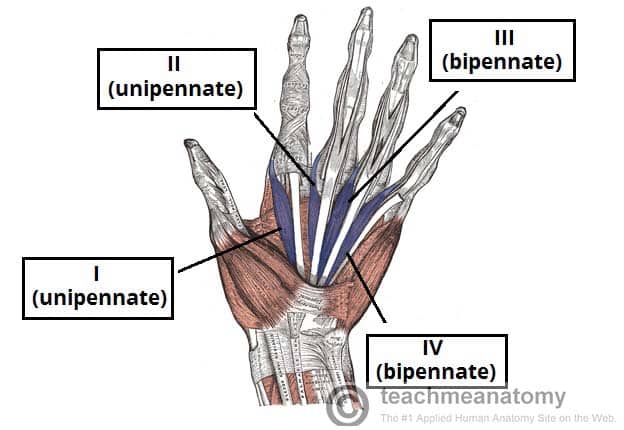
Muscles of the Hand
…and produce a forceful grip. Intrinsic muscles – located within the hand itself. They are responsible for the fine motor functions of the hand. In this article, we shall look…
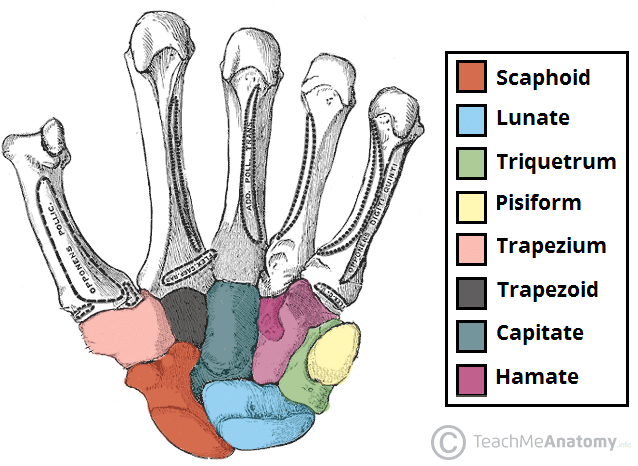
The Bones of the Hand: Carpals, Metacarpals and Phalanges
…at the anatomy of the bones of the hand – their structure, articulations and clinical correlations. By TeachMeSeries Ltd (2024) Fig 1 – Overview of the bones of the hand….
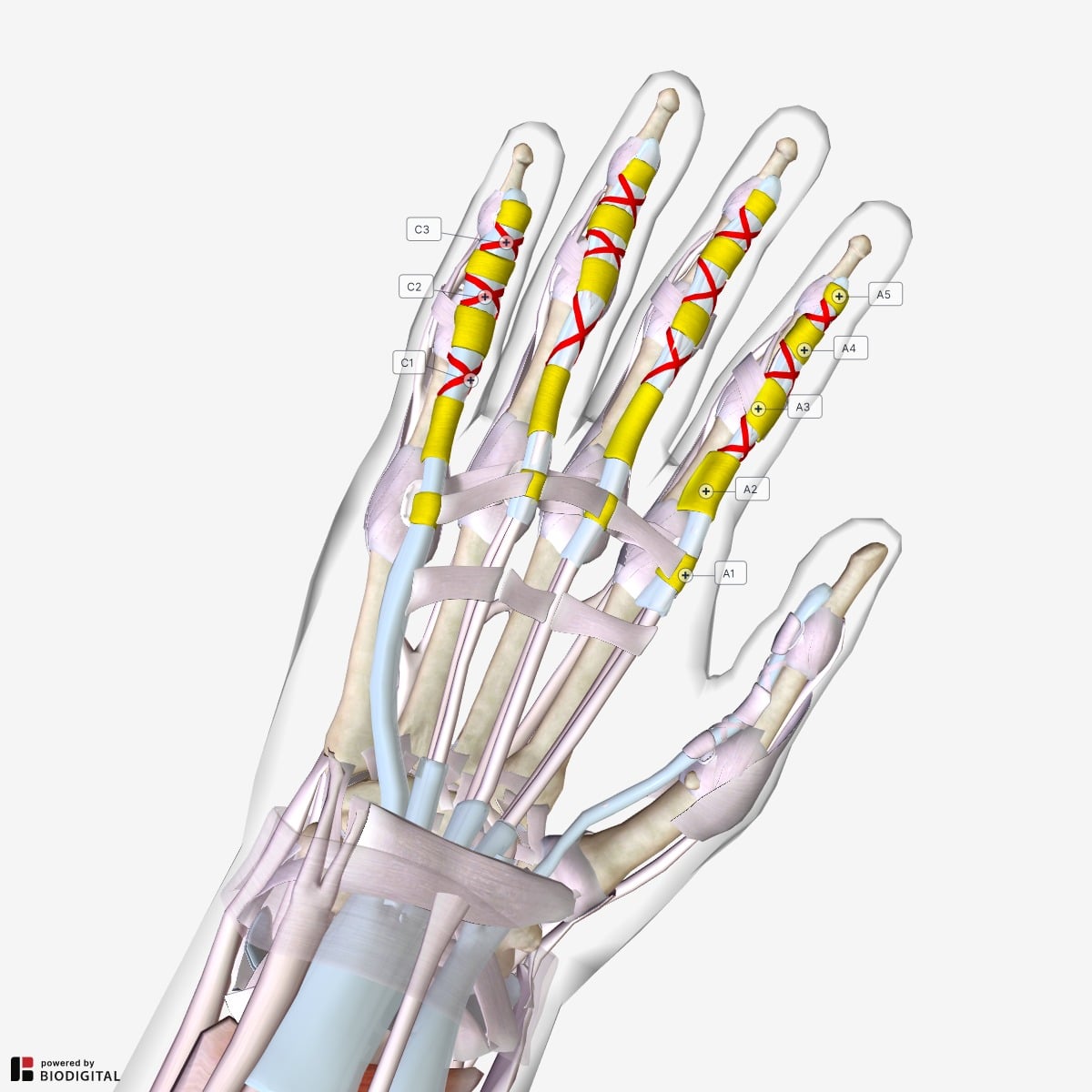
The Flexor Pulley System of the Hand
…These tendons enter the hand via the carpal tunnel, enclosed in a common synovial sheath. Within the hand, the tendons fan out and enter their respective fibrous flexor sheaths. These…
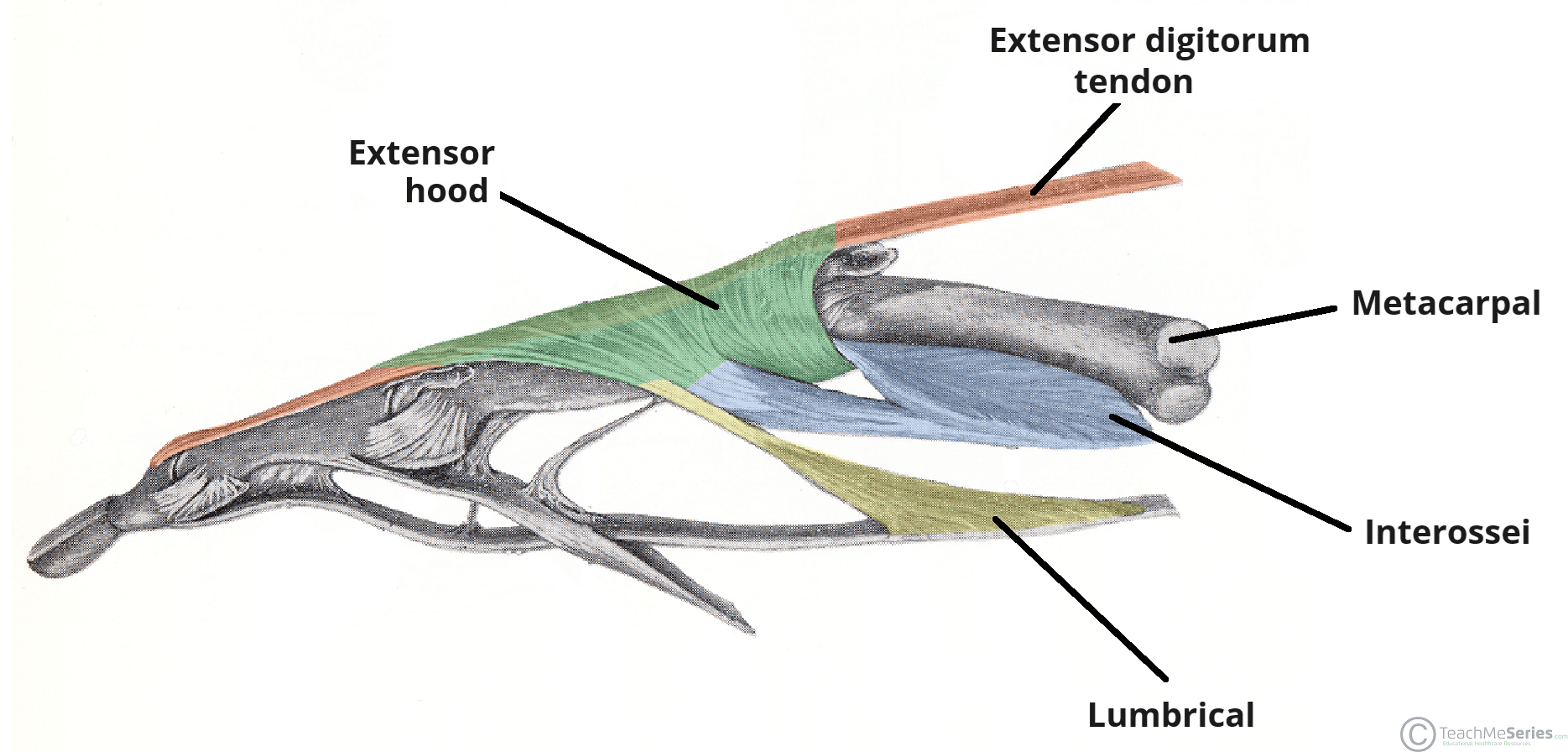
The Extensor Expansion of the Hand
The extensor expansion of the hand is a specialised connective tissue structure by which the extensor tendons insert onto the phalanges. It is a complex structure which acts to balance…
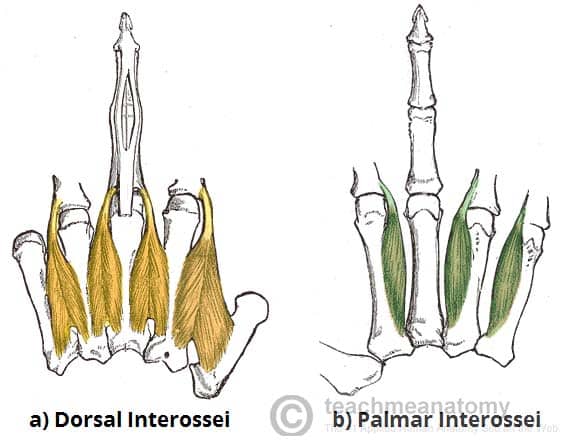
Dorsal Interossei (Hand)
The dorsal interossei are intrinsic muscles of the hand. They are located superficially on the dorsum of the hand, and can be palpated between the metacarpal heads. Attachments: Each interossei…
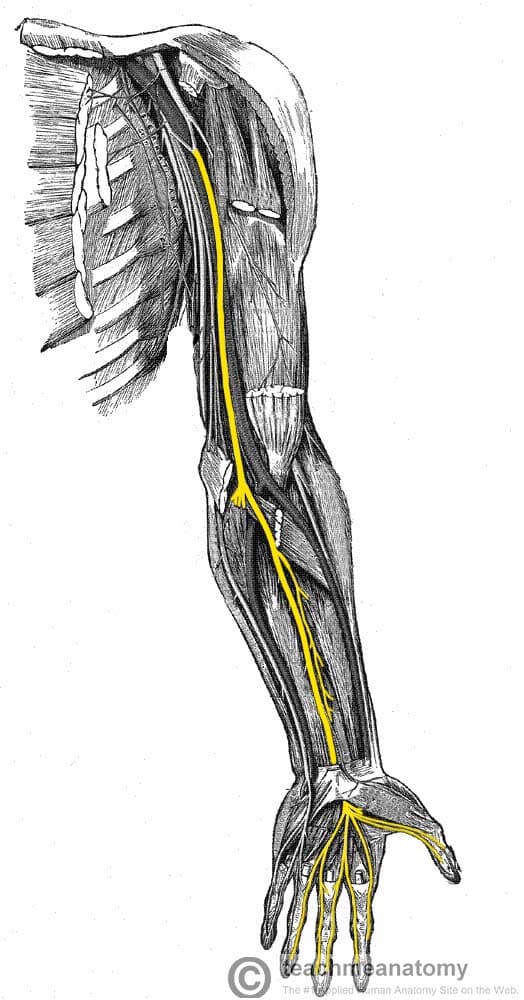
The Median Nerve
…pronation of the forearm, flexion of the wrist and flexion of the digits of the hand. Hand The median nerve innervates some of the muscles in the hand via two…
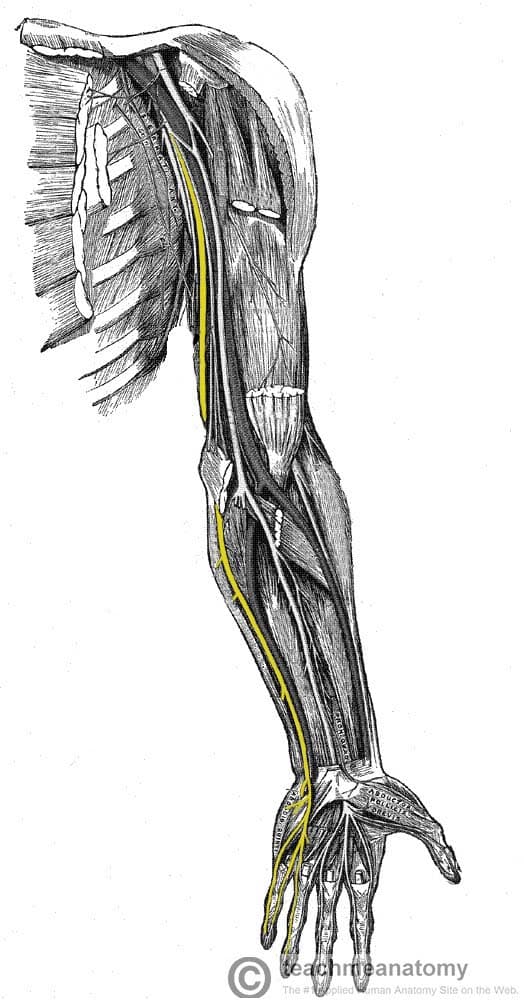
The Ulnar Nerve
…medial to the ulnar artery. It enters the hand via the ulnar canal (Guyon’s canal). In the hand, the nerve terminates by giving rise to superficial and deep branches. By…
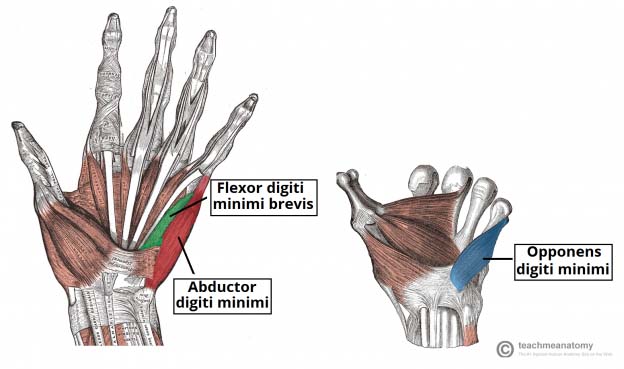
Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis (Hand)
The flexor digiti minimi brevis is a hypothenar muscle located within the hand. It is located lateral to the abductor digiti minimi brevis. Attachments: Originates from the hook of hamate…
Abductor Digiti Minimi (Hand)
The abductor digiti minimi is a hypothenar muscle located within the hand. It is the most superficial of the hypothenar muscles. Attachments: Originates from the pisiform and the tendon of…
Lumbricals (Hand)
The lumbricals are intrinsic muscles of the hand. There are four lumbricals – each associated with a digit. Attachments: Originates from the tendon of the flexor digitorum profundus. Inserts onto…